Here in this tutorial, we are going to set a dns (domain name system) server and a dhcp server. And then from our PC we will use dns service.
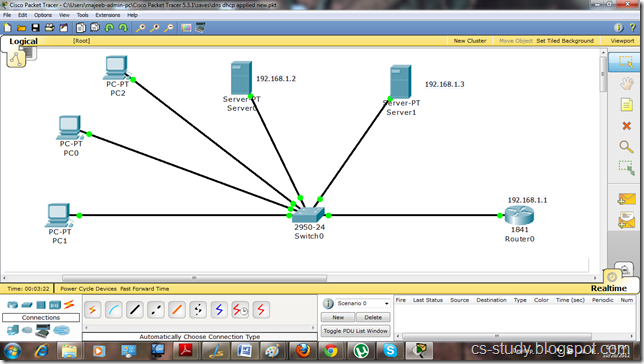
Server 0 in the above topology is our dhcp server and Server 1 is our dns server.
Set up IP on server 0.

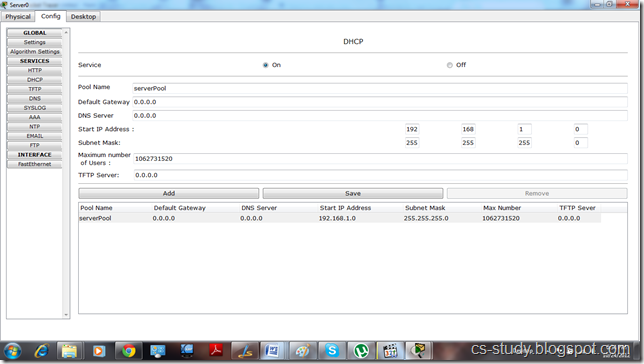
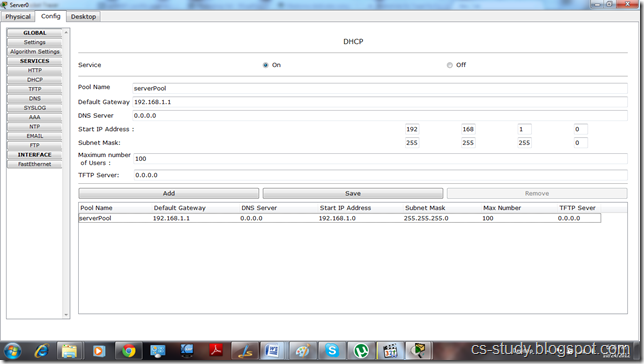
Set up DHCP on server 0.

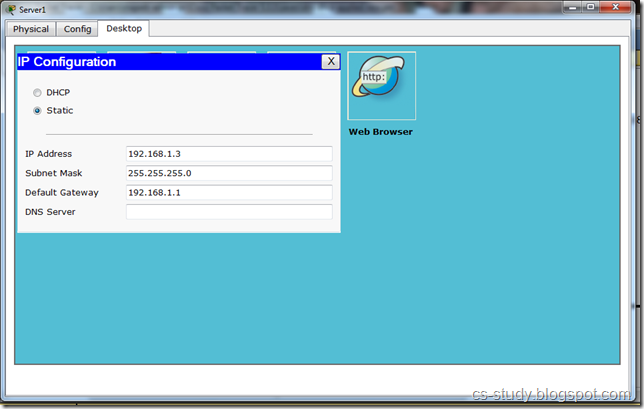
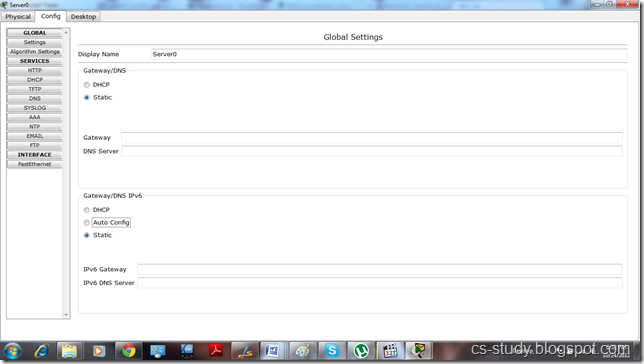
Set up IP on server 1.
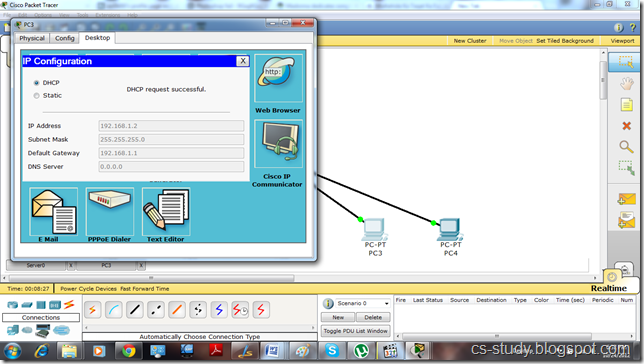
Now, go to PC and select DHCP.

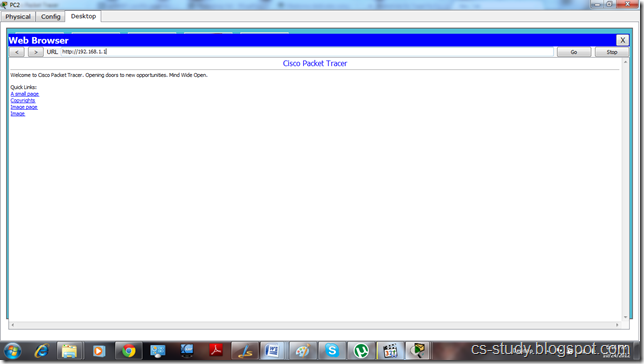
Go to Web Browser and enter Server 0 ip address. You can access the website of the server.
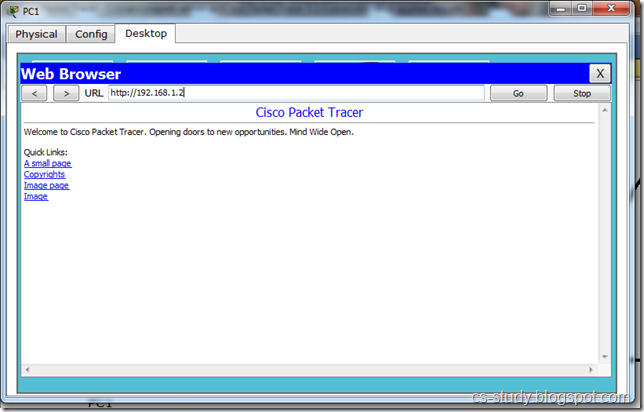
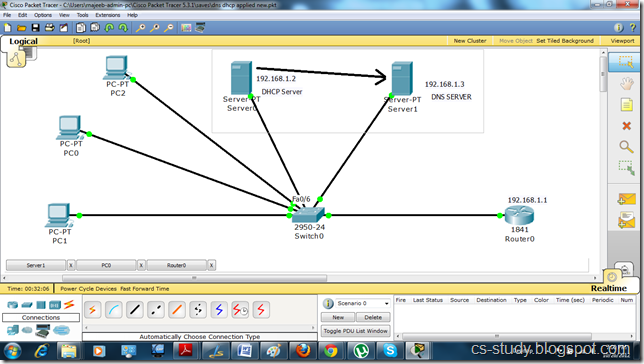
Now, let us set DNS on server 1.

Now, again go to PC and in the web browser enter the name that you set in DNS.
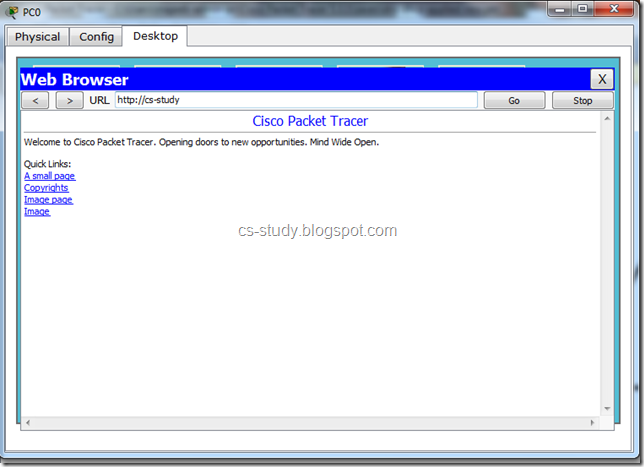
Voila, we have done it. Now, in this tutorial, router is additional and we can use it if required, Set the IP of the interface. Though i do not recommend to use this GUI panel for this.
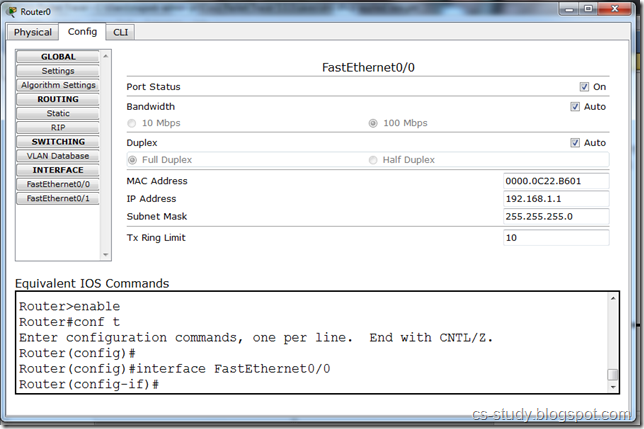
To see how to make a router DHCP server. Click here. You can also achieve DNS by using single sever by supplying the Server with the same IP and DNS address. Try it.

Server 0 in the above topology is our dhcp server and Server 1 is our dns server.

Set up IP on server 0.

Set up DHCP on server 0.

Set up IP on server 1.

Now, go to PC and select DHCP.

Go to Web Browser and enter Server 0 ip address. You can access the website of the server.

Now, let us set DNS on server 1.

Now, again go to PC and in the web browser enter the name that you set in DNS.

Voila, we have done it. Now, in this tutorial, router is additional and we can use it if required, Set the IP of the interface. Though i do not recommend to use this GUI panel for this.

To see how to make a router DHCP server. Click here. You can also achieve DNS by using single sever by supplying the Server with the same IP and DNS address. Try it.
Technorati Tags: dns and dhcp protocol on Packet Tracer,Packet tracer tutorial,Packet tracer networking,networking on Packet tracer,networking topology on Packet tracer,Packet tracer activity,dhcp on Packet Tracer,Dynamic host configuration protocol on Packet Tracer,education,networks,networking,Dynamic host configuration protocol on PT,dhcp on pt,dhcp,Dynamic host configuration protocol,dns on packet tracer











![clip_image002[7] clip_image002[7]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjzgHAfd9oMdDkTWxWgAVYfG2coC51eez42lzLSQRswo959UVQS9kcRyFcmT10SEksLkhcutHQdr0xRycGX4pckmjTR4MbHwu2zc527nIs_KtOQfHCumwSy3r4fuaEPmN7OXnpIpfOIa1s/?imgmax=800)