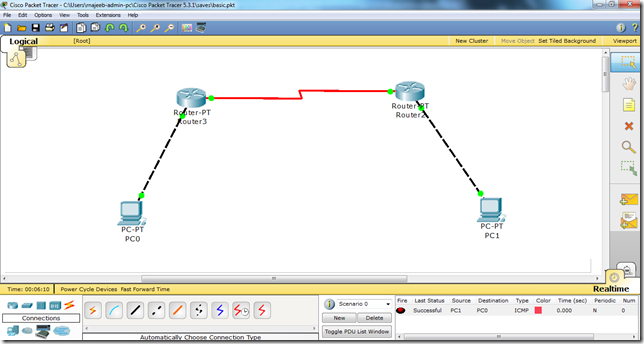
Router(config)# router rip

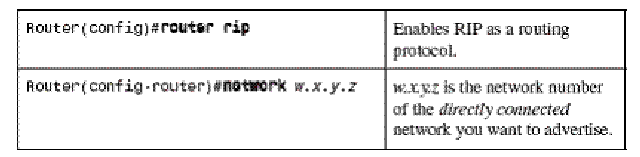


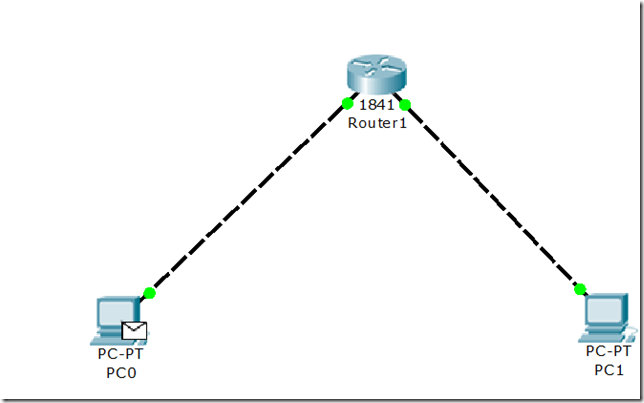





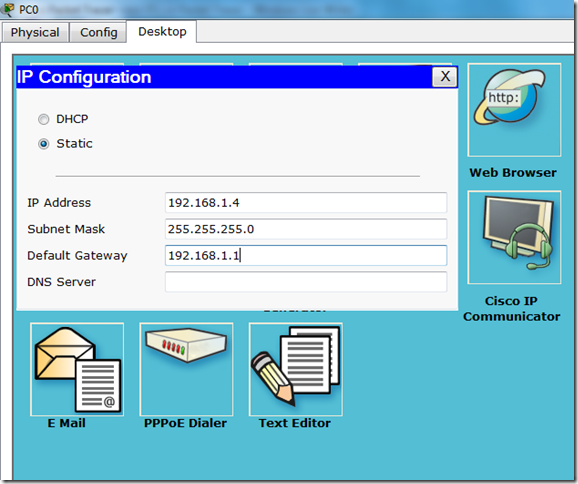
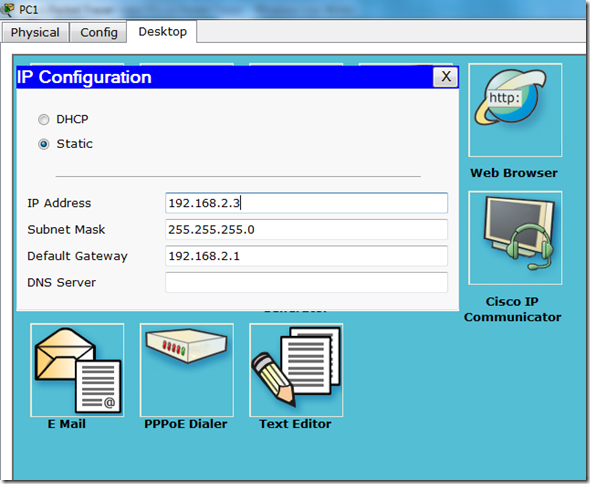
There are various common commands that one needs to be familiar with. These commands will be used all the time.
There are different modes. All modes have their own distinct commands.
All the configuration commands will be written in configuration mode.
Using the tab Key to Complete Commands
When you are entering a command, you can use the tab key to complete the command. Enter the first few characters of a command and press the tab key. If the characters are unique to the command, the rest of the command is entered in for you. This is helpful if you are unsure about the spelling of a command. For example, if we write in enable mode, “sh” and press tab button, “show” command will be written on the CLI mode.
Router Modes
TIP: There are other modes than these. Not all commands work in all modes. Be
careful. If you type in a command that you know is correct—show running-config, for example—and you get an error, make sure that you are in the correct mode.
Entering Global Configuration Mode
Configuring a Router Name
This command works on both routers and switches.
Configuring Passwords
These commands work on both routers and switches.
Here it is important to know that the enable secret password is encrypted by default. The enable password is not. For this reason, recommended practice is that you never use the enable password command. Use only the enable secret password command in a router or switch configuration. You cannot set both enable secret password and enable password to the same password. By doing so, it defeats the use of encryption.
Show Commands:
There are various show commands. in order to get familiar with these commands just write “show ?” in the enable mode.
Similarly, there are various commands that shows us the configurations that we have done on our router or any other device depending on the device we are working on. We will talk about later on.
Similarly, there are various commands in the configuration mode which we attain by entering the following command
Router# configure terminal.
Look at the following diagram.
Ok, so now lot of things are happening here. Red markers explain them, also we are setting the hostname of the router and we have successfully applied the password by the following command.
enable password cisco
Here, “cisco” is the password.
Similarly, the command
router#show ip interface brief
gives us the information about the interfaces of the router. Now, detail discussion on the interfaces will be done later.
Twisted Pair Cables:
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources; for instance, electromagnetic radiation from unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables, and crosstalk between neighboring pairs. In balanced pair operation, the two wires carry equal and opposite signals and the destination detects the difference between the two. This is known as differential mode transmission. Noise sources introduce signals into the wires by coupling of electric or magnetic fields and tend to couple to both wires equally. The noise thus produces a common-mode signal which is cancelled at the receiver when the difference signal is taken.
Categories Of UTP Cable:
It has been categorized into three categories based on the equipment that are being connected through these wires.
i. Straight Through Cable
ii. Cross Over Cable
iii. Roll Over Cable
Explanation:
Straight Through Cable:
Straight through cables are used to connect different devices like Switch to PC. Switch to Router. Router to Switch etc. Straight-through cables are used when each end of the communication transmits and receives on different pairs.
Cross Over Cable:
In a cross over the cable, the send and receive wires are "crossed over", meaning the wires are opposite on each end. This allows two PCs to talk to each other, has it connects the send of one computer to the receive of the other. Hence, the cross over cables are used to connect similar devices like PC to PC , Router to Router, Switch to Switch, Hub to Hub etc.
Roll Over Cable:
Roll over cables are used to connect to the console port of the device. It gets the name rollover because the pin outs on one end are reversed from the other, as if the wire had been rolled over and you were viewing it from the other side.
Transmission Pins:
Devices that transmit on 1,2 and receive on 3,6
1) PC
2)Router
3)Wireless Access Point AP
4) Networked printers
Devices that transmit on 3,6 and receive on 1,2
1)switch
2)bridge
3)hub 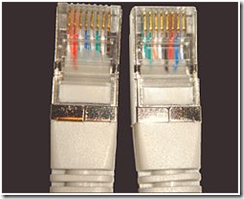
Required Equipment:
In order to make a network cable you need the following equipment.
i. Cat5, Cat5e cable.
CAT5 cable usually contains four pairs of copper wire, Fast Ethernet communications only utilize two pairs. A newer specification for CAT5 cable -CAT5 enhanced ("CAT5e" or "CAT 5e")- supports networking at Gigabit Ethernet[ speeds (up to 1000 Mbps) over short distances by utilizing all four wire pairs, and it is backward-compatible with ordinary CAT5.
ii. A connector named RJ-45.
RJ45 connectors feature eight pins to which the wire strands of a cable interface electrically. Standard RJ-45 pin outs define the arrangement of the individual wires needed when attaching connectors to a cable.
iii. Crimping tool:
Use to crimp the cable inside RJ 45 connector.
iv. Wire stripper or Knife:
You can use a knife too to cut the wire open. In order to make different combinations of it. we will have to cut the upper protective coating and bring out the eight wires.
| Category | Speed | Use |
| 1 | 1 Mbps | Voice Only (Telephone Wire) |
| 2 | 4 Mbps | LocalTalk & Telephone (Rarely used) |
| 3 | 16 Mbps | 10BaseT Ethernet |
| 4 | 20 Mbps | Token Ring (Rarely used) |
| 5 | 100 Mbps (2 pair) | 100BaseT Ethernet |
| 5e | 1,000 Mbps | Gigabit Ethernet |
| 6 | 10,000 Mbps | Gigabit Ethernet |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void main() { FILE *fptr; char filename[15]; char ch; ...