The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a data link protocol commonly used in establishing a direct connection between two networking nodes. It can provide connection authentication, transmission encryption and compression. PPP is used over many types of physical networks including serial cable, phone line, trunk line, cellular telephone, specialized radio links, and fiber optic links etc. Internet service providers (ISPs) have used PPP for customer dial-up access to the Internet, since IP packets cannot be transmitted over a modem line on their own, without some data link protocol. PPP is commonly used as a data link layer protocol for connection over synchronous and asynchronous circuits, where it has largely superseded the older Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) and telephone company mandated standards (such as Link Access Protocol, Balanced (LAPB).
PPP was designed somewhat after the original HDLC specifications. The designers of PPP included many additional features that had been seen only in proprietary data-link protocols up to that time.
HDLC
HDLC provides both connection-oriented and connectionless service. HDLC can be used for point to multipoint connections, but is now used almost exclusively to connect one device to another, using what is known as Asynchronous Balanced Mode (ABM).
A password authentication protocol (PAP) is an authentication protocol that uses a password. PAP is used by Point to Point Protocol to validate users before allowing them access to server resources. Almost all network operating system remote servers support PAP.
PAP transmits unencrypted ASCII passwords over the network and is therefore considered insecure. It is used as a last resort when the remote server does not support a stronger authentication protocol, like CHAP or EAP (the latter is actually a framework).
Password-based authentication is the protocol that two entities share a password in advance and use the password as the basis of authentication. Existing password authentication schemes can be categorized into two types: weak-password authentication schemes and strong-password authentication schemes. In general, strong-password authentication protocols have the advantages over the weak-password authentication schemes in that their computational overhead are lighter, designs are simpler, and implementation are easier, and therefore are especially suitable for some constrained environments.
PAP works basically the same way as the normal login procedure. The client authenticates itself by sending a user name and an (optionally encrypted) password to the server, which the server compares to its secrets database. This technique is vulnerable to eavesdroppers who may try to obtain the password by listening in on the serial line, and to repeated trial and error attacks.
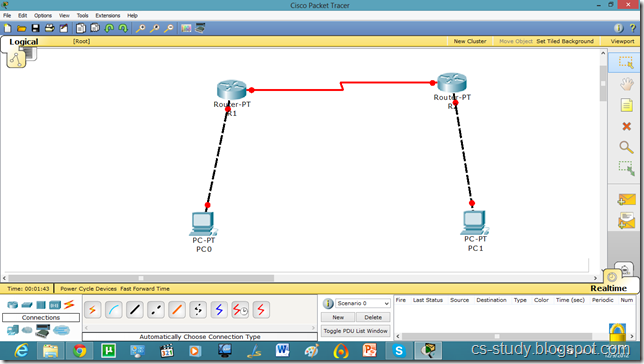
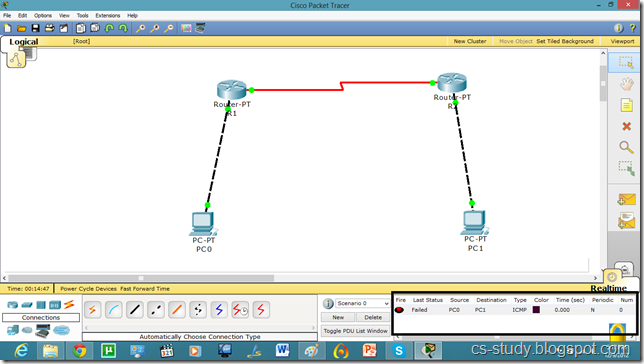
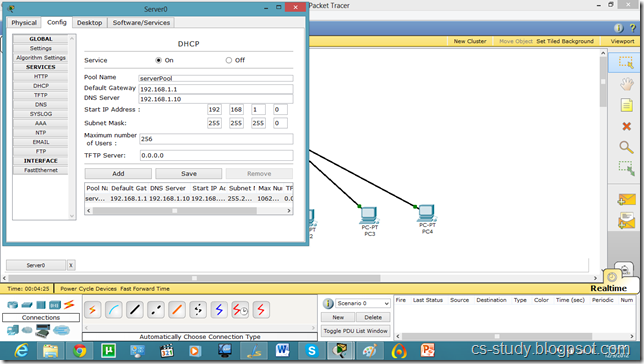
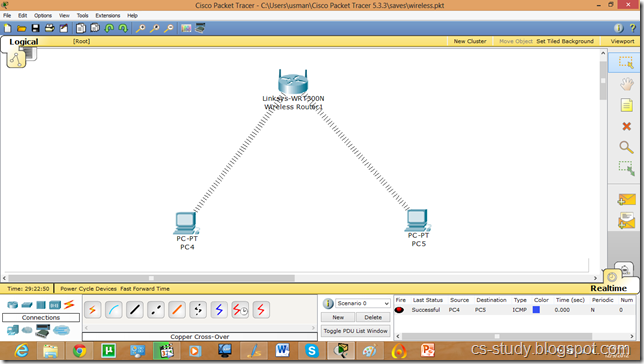
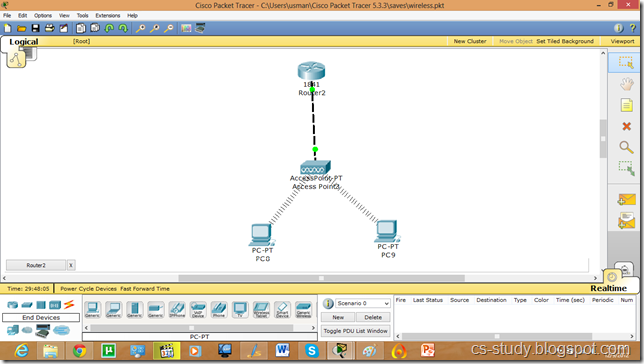
Let us apply PPP on packet tracer. Consider the following simpler topology.

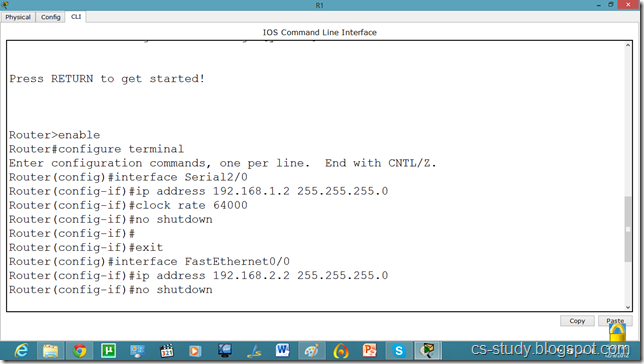
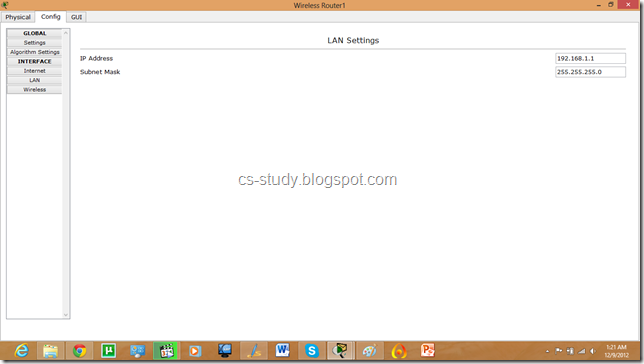
Let us apply IP addresses on the interfaces and change the state of the interface from down to UP. So that they can communicate.

Similarly, for serial interface.

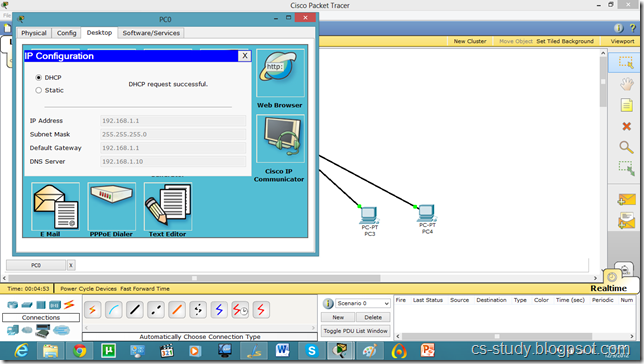
PC IP setup

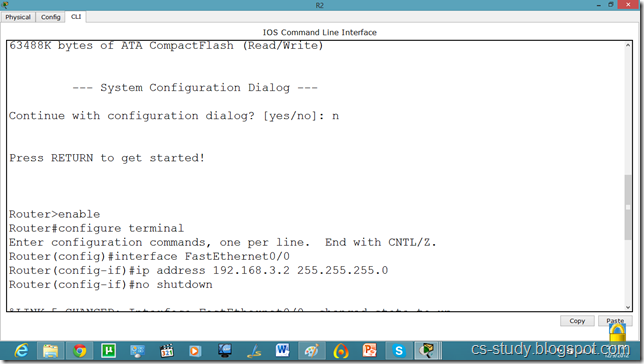
The IP configuration on other router.

serial int setup.

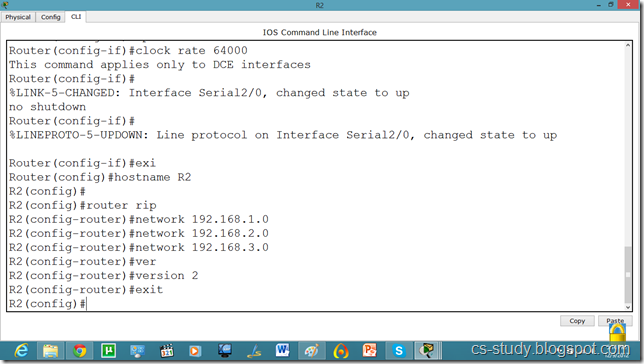
Now, we know that PCs that are attached cannot communicate until we apply a routing mechanism. In this case we are applying the RIP V2 protocol. Apply the following set of commands on both routers. We have also set the hostname of the router which will be useful to us later.
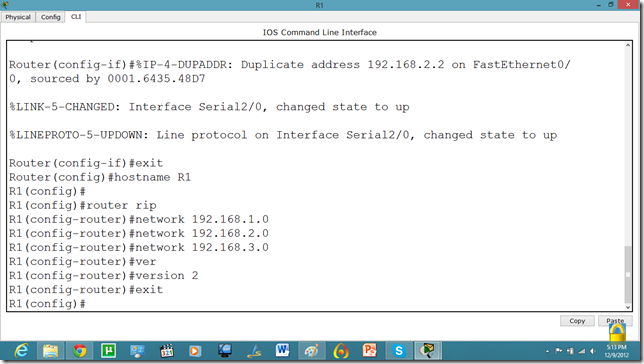
Now, let us set the commands on the second router as well.

Now, both PCs can communicate.

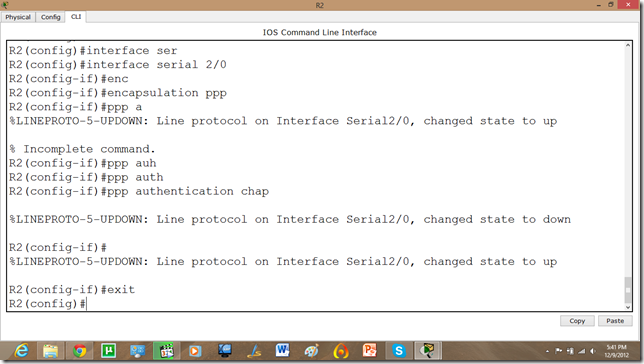
Now, we will set the authentication, In this tutorial we are going to apply PAP.
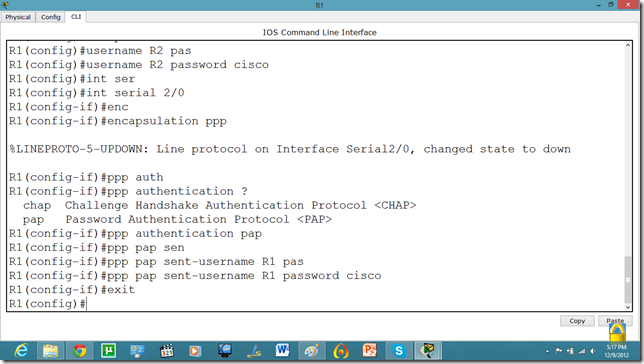
As we set the authentication on one router the communication is disabled.

Let us set it on other router as well.
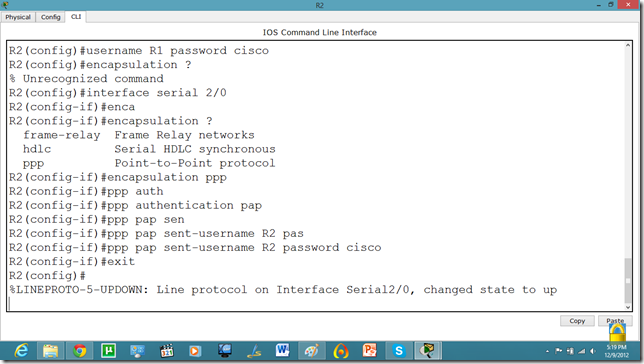
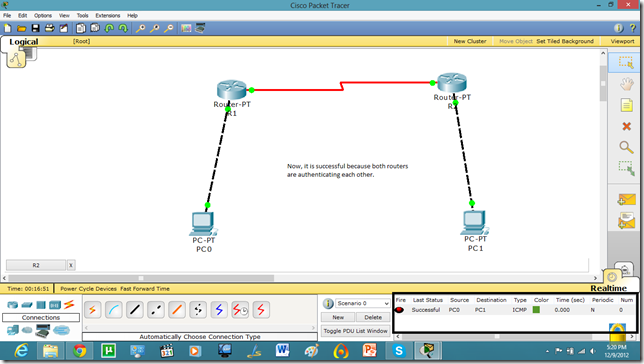
Now, they can communicate.
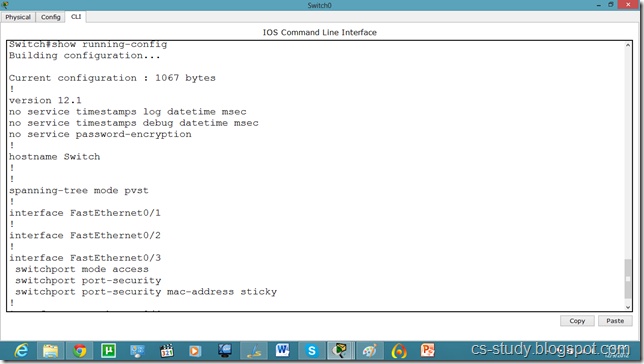
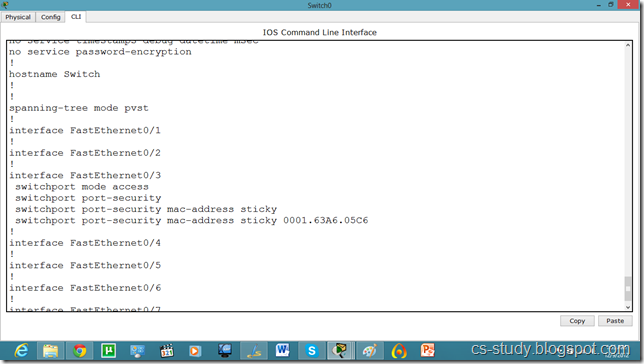
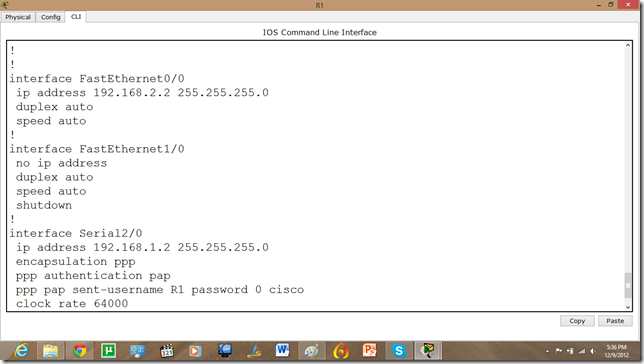
Now, if we run show run command in enable mode. We can see the authentication enabled in router.
Technorati Tags: packet tracer tutorial,pt tutorial,pap on packet tracer,ppp on packet tracer,password authentication protocol on packet tracer,password authentication protocol on pt,password authentication protocol,point to point protocol on packet tracer,point to point protocol tutorial,point to point protocol